Revitalizing China's Intangible Cultural Heritage
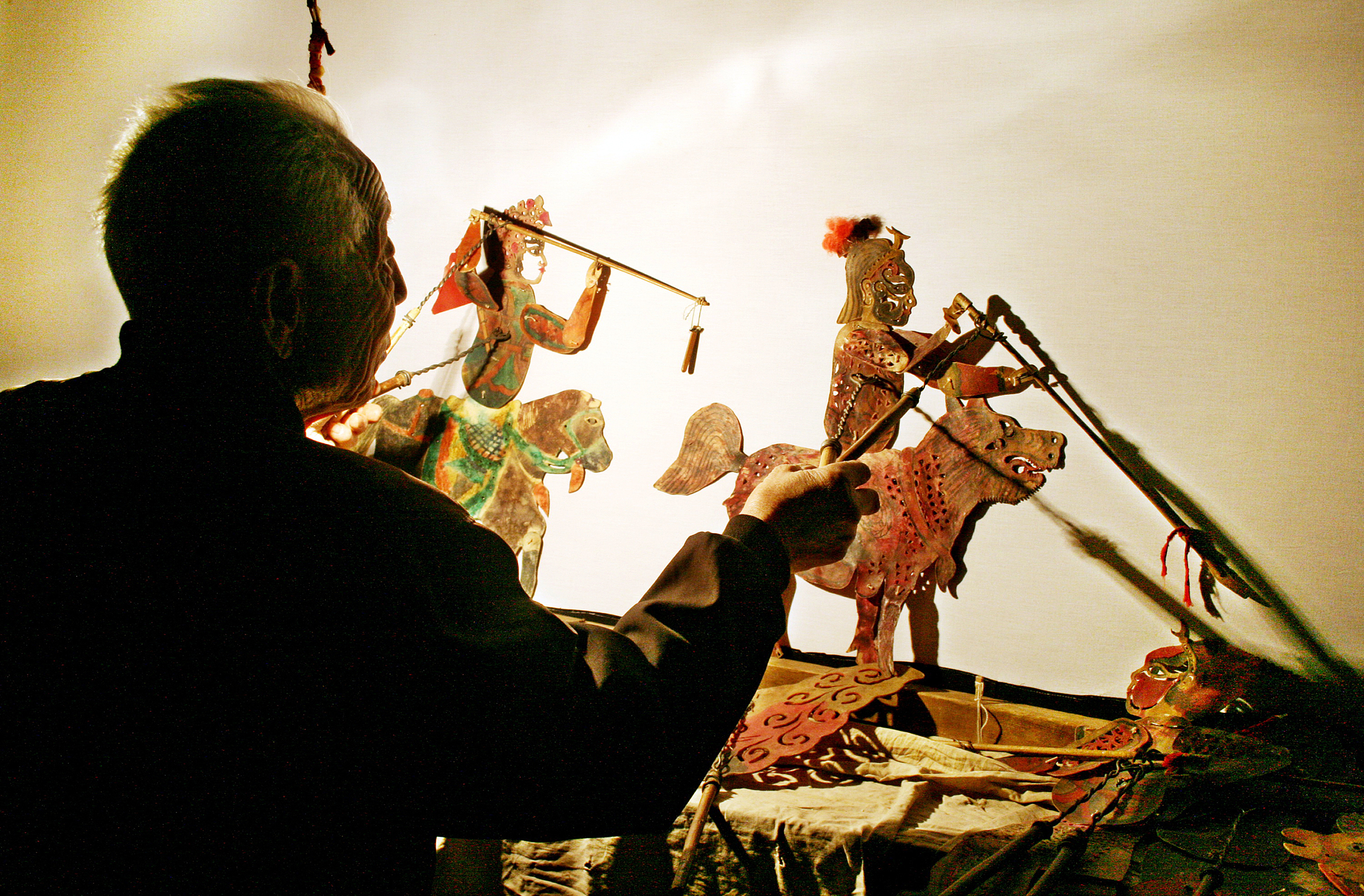

PHOTO:?VCG
By LIN Yuchen
China's Spring Festival serves as a vibrant stage for showcasing the nation's rich intangible cultural heritage (ICH). On the auspicious day of the Lunar New Year, an increasing number of ICH projects are taking center stage, captivating audiences nationwide.
From the recent show of a nation-level lion dance team in Beijing's Beihai Park, to the live demonstrations by nearly 30 ICH inheritors at Nanjing's Confucius Temple, Chinese traditional cultural heritage is fused with new technologies that adds colorand joy to the lives of Chinese.
Creating phenomenal cultural products
The fusion of modern technology with ICH has given rise to a new era of cultural innovation.?From the integration of holographic projection art installations at Beijing's Drum Tower and the technology charged “Omni-Chang’an" Shaanxi folk art performance in Xi'an, Shaanxi province, to the use of 3D printing and AI in crafting intricate Tang Dynasty figurines in Zigong city, Sichuan province, the synergy of tradition and technology has birthed a series of phenomenal cultural products.
Meanwhile, in Luoyang city, Henan province, Gao Shuiwang, a representative inheritor of the national-level ICH Tang Tri-Color Glazed Ceramics, is leveraging the power of the Internet to revitalize ancient craftsmanship. Using 3D technology and AI, Gao has recreated the lost Tang artifacts such as horses, camels, vessels, and figurines, bringing them back to life in stunning detail.
These technologically infused cultural creations are not confined to museums but are also being brought into schools and communities, enriching people's daily lives with the beauty of Tang Tri-Color Glazed Ceramics.
According to Yang Hong, professor and director of the Intangible Cultural Heritage Communication Research Center at the Communication University of China, legislation in the country has been enacted to specify measures such as inheritance and dissemination to protect intangible cultural heritage.
Bridging tradition and modernity
Technology not only preserves ICH but also empowers its inheritors to bridge the gap between tradition and modernity. Through the innovative use of VR experiences and interactive digital archives, younger generations are gaining unprecedented access to traditional crafts like shadow puppetry.
Moreover, technological advancements, such as 3D printing and AI, are enabling artisans like Li Changqing to revitalize ancient crafts like Sichuan's Qinzhai clay sculptures, attracting a new wave of enthusiasts and ensuring the continued legacy of these cherished traditions.
In addition to individual artisans, collaborative initiatives between technology companies and cultural institutions have also played a significant role in empowering cultural inheritors.
For example, the collaboration between Tencent Cloud and the Gansu Provincial Department of Culture and Tourism has resulted in the development of a big data platform targeting the ICH of Gangsu, which digitizes, preserves, and showcases a wide range of ICH resources. The platform not only facilitates the preservation and promotion of Gansu's cultural heritage but also provides economic opportunities for local artisans and communities.
Ensuring the future of preservation
According to Li Qiong, a teacher at Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, certain ICH projects face challenges such as high technical difficulty, intense labor, lengthy duration, and low income, leading to a scarcity of willing learners. “To address this, various measures must be implemented to enhance the social and economic status of inheritors,” said Li.
Such measures are being implemented,for example, to preserve Suzhou embroidery, usually considered the best of all Chinese hand embroideries. According to Yao Jianping, an inheritor of Suzhou embroidery, “Nowadays government departments have revitalized the embroidery industry in ethnic areas through training and setting up classes and long-term twinning, and a large number of villagers have been able to make a good living through their manual labor.”
In addition to policy support, online platforms, such as live streaming and short video apps, have become popular channels for promoting traditional crafts and engaging with younger audiences, further revitalizing the cultural heritage sector and ensuring its sustainability in the digital era.